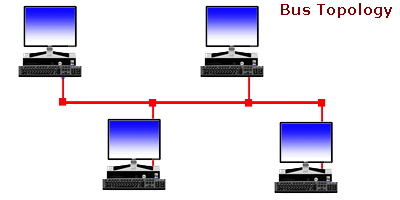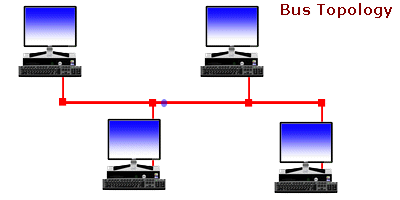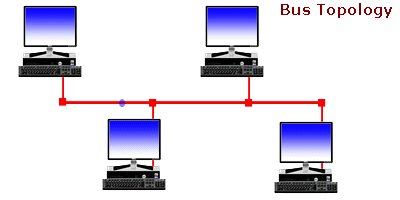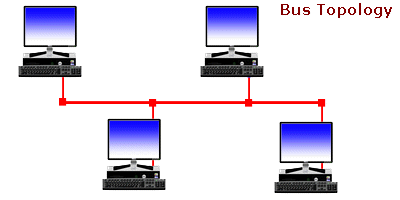
A bus topology is a topology for a Local Area Network (LAN) in which all the nodes are connected to a single cable. The cable to which the nodes connect is called a “backbone”. If the backbone is broken, the entire segment fails. Bus topologies are relatively easy to install and don’t require much cabling compared to the alternatives.
Advantages (benefits) of Linear Bus Topology
1) It is easy to set-up and extend bus network.
2) Cable length required for this topology is the least compared to other networks.
3) Bus topology costs very less.
4) Linear Bus network is mostly used in small networks. Good for LAN.
Disadvantages (Drawbacks) of Linear Bus Topology
1) There is a limit on central cable length and number of nodes that can be connected.
2) Dependency on central cable in this topology has its disadvantages.If the main cable (i.e. bus ) encounters some problem, whole network breaks down.
3) Proper termination is required to dump signals. Use of terminators is must.
4) It is difficult to detect and troubleshoot fault at individual station.
5) Maintenance costs can get higher with time.
6) Efficiency of Bus network reduces, as the number of devices connected to it increases.
7) It is not suitable for networks with heavy traffic.
8) Security is very low because all the computers receive the sent signal from the source.
References:
ianswer4u.com.(2019). ianswer4u.com .Retrieve.<November 6,2019,2:57PM>.from.https://www./2011/05/bus-topology-advantages-and.html
techopedia.com.(2019).techopedia.com.Retrieve.<November 6,2019,2;57PM>.from.https://www.techopedia.com/definition/17045/bus-topology
